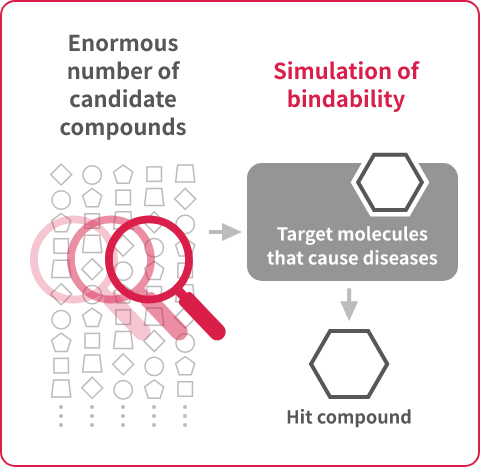
The process of research involves obtaining a hit compound (a compound that can readily bind to a disease-causing target molecule) and optimizing it into a drug candidate compound (a compound with enhanced suitability as a drug). This used to be a costly and time-consuming process, but Astellas is working to improve it through the implementation of DX.
Ultra Large scale Virtual Screening
By performing high-speed calculations and assessing a larger number of compounds, we can obtain potent hit compounds in a short period of time. In the past, calculations were performed on approximately one million compounds using an internal server. It would have been possible to obtain more potent hit compounds if we were to evaluate hundreds of millions of compounds. However, the process would have required one to two years on the conventional system. We have updated our system by combining cloud computing with AI that predicts ease of binding. Now, we can complete calculations for hundreds of millions of compounds in as short as one to two weeks.
“Human-in-the-Loop” Drug Discovery Platform
Furthermore, we are also working to shorten the research time to optimize acquired hit compounds into high-quality drug candidates. We installed AI and robots to accelerates revolving a DMTA cycle where we "Design" and "Make" the compound, "Test" the effects, "Analyze" the information, and design better compounds for the next cycle based on the results obtained from the previous cycle. The speed of drug discovery has been dramatically improved by integrating AI and robots into each step, with researchers adding value in the form of ideas and comprehensive judgment at key stages. Using this platform, we have reduced the time it takes from hit compound to acquisition of a drug candidate compound by approximately 70% in successful cases.
In order to utilize this platform for new modalities such as cells and genes, the robot Mahol-A-Ba is being used in the Test phase to evaluate pharmacological effects.
Astellas DX Strategy Series Vol.2: Drug Discovery Platform Integrating Humans, AI, and Robots
Read moreE-PaD: A Research Support Tool that Uses NLP
E-PaD helps provide insights necessary for drug discovery research and assists in generating new ideas for drug discovery. It uses an AI technology called NLP (Natural Language Processing) to efficiently extract meaningful information on pathology, genes, biology, modalities, etc., from the life science literature, which grows by more than 1.6 million every year. The tool not only performs simple keyword searches but also suggests highly relevant disease (indication) candidates with rationales to researchers based on the content of sentences and phrases related to biology, etc. E-PaD also has a function to consolidate and visualize information on the external environment, and can support planning of research strategy based on competitive landscape and life science trends.
Related links