Business Risks
(1) Identifying and Mitigating Risks Relating to the Performance of Business Activities
As a pharmaceutical company operating globally, Astellas is expected to follow various regulations with a high level of compliance. In addition, Astellas must also address various risks that could impact its business results and reputation. In FY2019, Astellas established the Global Risk and Resilience Management Committee with the aim of further developing the risk management activities. Since then, Astellas continues to operate Enterprise Risk Management and strives to make further improvement.
Under Enterprise Risk Management, risks are identified on the Group-wide level and on the individual division level. Those risks are classified and prioritized using a consistent evaluation process and, if deemed necessary, results in the development of a universal means to address these risks. Identified risks are regularly evaluated by the Global Risk and Resilience Management Committee, and measures to address high priority risks are discussed at the Executive Committee, chaired by the Representative Director, President and CEO.
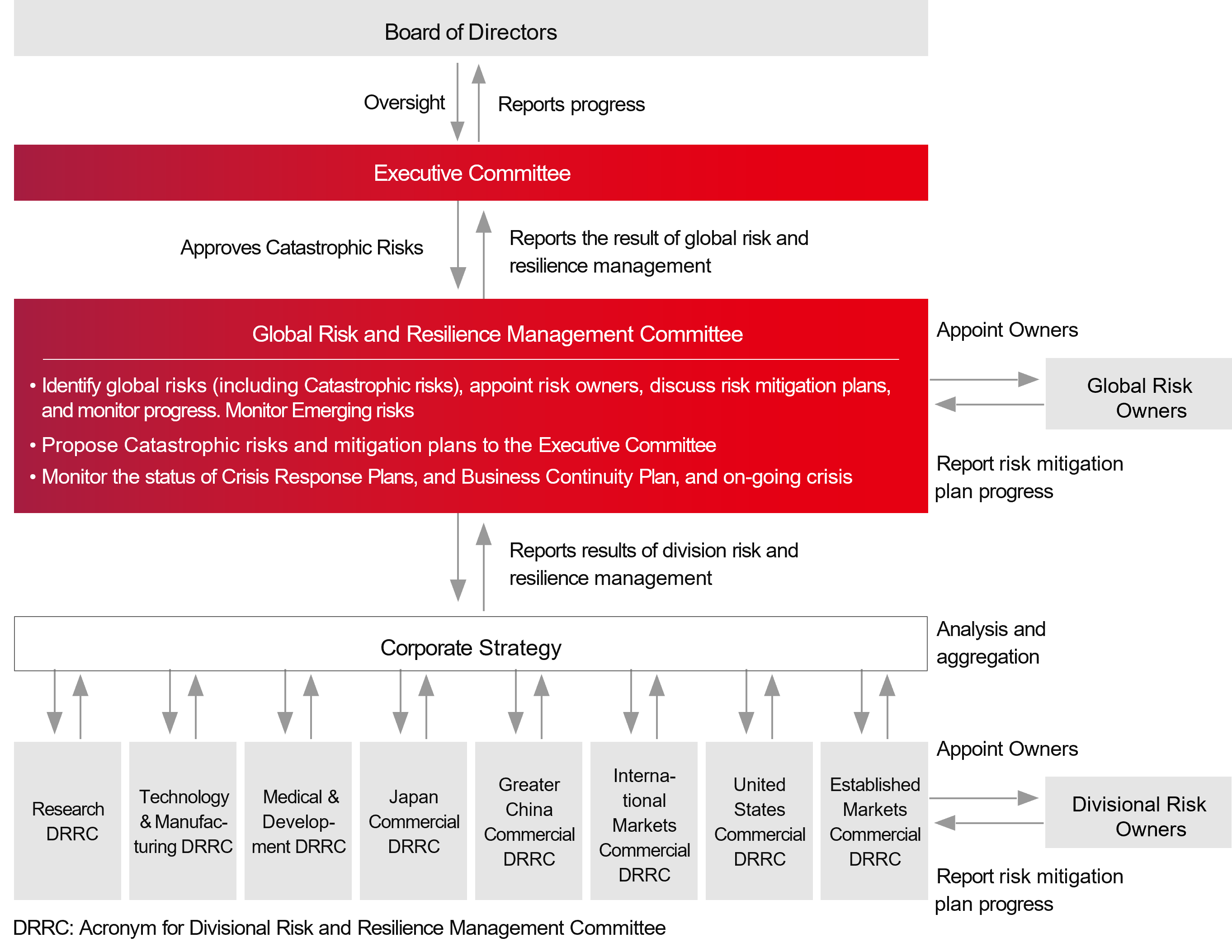
(2) Risk Management System
The diagram below summarizes Astellas’ risk management system.
(3) Catastrophic Risks
The risks identified by management as having the potential to have a considerable impact on financial position, business results and cash flow position of the consolidated companies are mainly set forth below.
Any forward-looking statements are based on judgments at the end of FY2023.
1 Risks related to cybersecurity
In recent years, the technology involved in cyberattacks is advancing at an unprecedented level and the methods of attack are growing more diverse and sophisticated. In light of this environment, Astellas has identified risks related to cybersecurity as a Catastrophic risk. DigitalX Division is leading the response to this risk, implementing various countermeasures against cyberattack on a global basis that includes monitoring of networks and facilities, and taking every precaution to manage the risk.
However, in the event that business is substantially interrupted due to a cyberattack or serious system failure despite having such measures in place, or in the event that important data, including personally identifiable information, is lost, corrupted or leaked externally, the Astellas Group’s business results may be significantly affected.
In addition to the above Catastrophic risks identified by the Astellas Group, there are many other risks. Some risks are unique to the pharmaceuticals business, such as the uncertain nature of research and development, the risk of being infringed upon or infringing intellectual property rights, risk of drug side effects or safety issues arising thereof, and the risk of Astellas Group business’ partial dependence on licensing and sales of third-party developed drugs. Other risks include the infringement of related laws and regulations (e.g., competition with rival products, environment, health and safety); commercial litigations; delays or stoppages in manufacturing due to natural disasters; and exchange rate fluctuations. Such risks may affect the Astellas Group’s business results and financial position.
Please note that this does not constitute a comprehensive list of all risks relating to the Astellas Group.